Fingerprint Safe Box,Residential Safe,Biometric Safe Box,Steel Safe Box Hebei Yingbo Safe Boxes Co.,Ltd , https://www.yingbosafes.com
In the direct detection method, the enzyme is directly attached to the primary antibody (Figure 1.5). The operation is simple and the detection steps are small. Although direct detection is fast and straightforward, it tends to be less sensitive than indirect detection because fewer steps can occur in signal amplification during this process. In addition, direct labeling of the enzyme to the primary antibody may result in cost and resource constraints.
Indirect Western blot detection methods <br> Indirect detection methods are more popular than direct detection methods, mainly with higher sensitivity. An antibody that recognizes an antigen of interest by indirect detection is called a primary antibody (Figure 1.5). Detection is achieved by the addition of a labeled secondary antibody that recognizes a specific epitope on the primary antibody. Such epitopes are typically species-specific; for example, several different primary antibodies produced in rabbits can be recognized by the same anti-rabbit antibody. 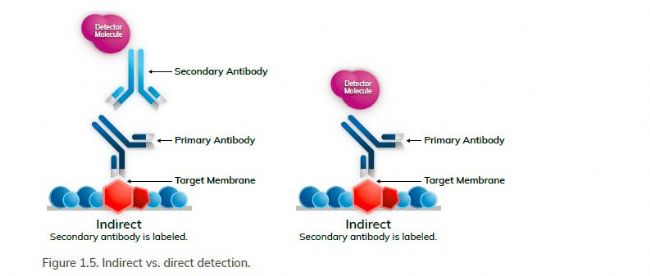
Antibody quality and type <br> One of the main factors affecting the results of Western blot is the quality of the antibody, especially the quality of the primary antibody. High quality antibodies - high specificity, high binding affinity and low background - increase the specificity and sensitivity of the assay, both monoclonal and polyclonal primary antibodies are available.
<br> a polyclonal anti - polyclonal antibodies using the body's immune response to the antigen of interest is obtained. They are isolated directly from the serum of immunized animals, usually rabbits, goats, donkeys or sheep, and are therefore a complex mixture of all antibodies produced by animals. During an immune response, a single B cell produces an antibody that recognizes a particular epitope on the antigen, and antibodies produced by different B cells recognize different epitopes. Since polyclonal antibodies recognize different sites on the antigen, multiple antibodies can bind to the antigen at the same time, making the polyclonal antibody more sensitive than the monoclonal antibody. However, this broad binding specificity sometimes results in a higher background signal for polyclonal antibodies.
The monoclonal antibody-monoclonal antibody is collected from the supernatant of a hybridoma cell line which is a cell line obtained by fusing a single antibody synthesis cell with a myeloma cell. These cell lines are usually derived from mice or rats. Since a single antibody producing cell or clone is used, the hybridoma cell line produces the same antibody and recognizes the same epitope on the antigen. Monoclonal antibodies are weaker than polyclonal antibodies because monoclonal antibodies bind only to a single protein
Secondary antibodies <br> There are many types of secondary antibodies that can be used for Western blotting. The type of secondary antibody used depends on the type and type of primary antibody, the method of detection, etc. The type of primary antibody - the type of monoclonal primary antibody and Types are typically derived from mouse or rat cells, while polyclonal antibodies can be isolated from a variety of animals. The secondary antibody must have recognition specificity for the primary antibody species. Therefore, the anti-mouse or rat secondary antibody must be used simultaneously with the monoclonal antibody, and when the primary antibody is isolated from the rabbit, an anti-rabbit secondary antibody should be used. Depending on the type of heavy chain molecule and light chain molecule that make up the antibody, antibodies can be divided into different classes and subtypes (also known as isotypes). The secondary antibody must match the primary antibody class or subtype for proper identification. Secondary antibodies that recognize all classes (ie, all mouse IgG antibodies) or specific classes (eg, mouse IgG2a) can be purchased. Secondary antibodies with specific subtypes are also useful for detecting multiple proteins simultaneously, as each secondary antibody can have a different label.
Specific secondary antibody
Anti H+L - anti-heavy and light chain antibodies (H+L) are specific for both the heavy and light chain portions of the protein of interest. This type of secondary antibody is usually used when the type of primary antibody is unknown.
Light chain specificity - When Western blotting is performed after immunoprecipitation, antibodies that recognize only the light chain portion of the antibody are typically used. Use this antibody to prevent the identification of heavy chains that precipitate antibodies
Antibody Purification <br> Both Primary and Secondary Antibodies Can Purify Reduce Background Signal Affinity Purification - Affinity Purification Affinity columns are used to remove antibodies that do not bind to the desired epitope. Affinity-purified antibodies have higher specificity because there are fewer target-exposed antibodies.
Pre-adsorbed-pre-adsorbed antibodies can also be used to increase the specificity of binding and reduce cross-reactivity. For example, rabbit anti-IgG antibodies may be pre-adsorbed on IgG of mice, rats and goats to prevent recognition of other types of IgG. Pre-adsorbed antibodies are highly specific and are recommended for multiple Western blotting.
Antibody labeling
An important consideration when selecting a primary (direct detection) or secondary (indirect detection) antibody is the type of label that binds to the antibody. Enzyme labeling (for chemiluminescence or film detection), fluorescent labeling or other small molecules (biotin) for amplifying signals.
Enzyme Labeling - The two most commonly used enzymes are alkaline phosphatase (AP) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP). Many antibodies can be labeled with enzymes, which makes such antibodies very popular. Since it is an enzymatic reaction, it is necessary to control the exposure to acquire a signal. Chemiluminescence has a supersaturation limit that limits the dynamic range of detection. 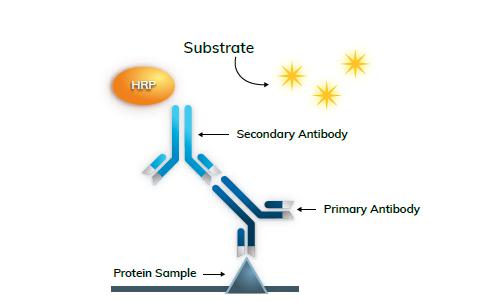
 Other markers - biotinylated antibodies can be used for sensitive detection of low abundance proteins. This system relies on strong binding between biotin and fluorescently labeled (or chemiluminescent label) avidin/streptavidin. Detection antibodies typically bind to multiple biotin molecules, and when multiple labeled avidin/streptavidin molecules bind to biotin molecules, a strong signal is produced.
Other markers - biotinylated antibodies can be used for sensitive detection of low abundance proteins. This system relies on strong binding between biotin and fluorescently labeled (or chemiluminescent label) avidin/streptavidin. Detection antibodies typically bind to multiple biotin molecules, and when multiple labeled avidin/streptavidin molecules bind to biotin molecules, a strong signal is produced.
Direct or indirect western blot detection antibody introduction
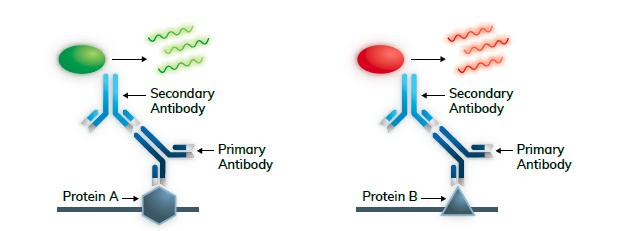
Direct western blot detection When multiple secondary antibodies are combined with a single primary antibody, this increases the sensitivity of the detection and increases the flexibility of detection because the type of label used to detect the secondary antibody can be easily changed. Fluorescent labeling - Detection antibodies can also be labeled directly with fluorophores and detected using a fluorescence detection system. The fluorophore emits light of a slightly longer wavelength under excitation of light of a suitable wavelength. The emitted light is then captured by the imager and converted into a digital signal. Unlike the enzyme-dependent detection method, the light emitted by the fluorophore is uniform and proportional to the amount of protein on the membrane to achieve accurate quantification.